Background
The Bulk Power System
Four major electric system networks serve the United States and Canada. Two major networks, the Western Interconnection and Eastern Interconnection, are divided roughly where the Rocky Mountains meet the Great Plains. Quebec and most of Texas are served by their own interconnections. There are physical asynchronous connections between the Western, Eastern, and Texas interconnections, but little if any electricity is exchanged between them. The generating resources and high-voltage transmission equipment that make up these networks constitute the bulk power system (BPS). Together these components generate and deliver electricity to customers across North America. The BPS does not include local distribution systems, which generally operate at lower voltages.
Six Regional Entities have responsibility delegated by NERC for ensuring BPS reliability within their respective footprints. WECC is the Regional Entity responsible for the Western Interconnection.
.png)
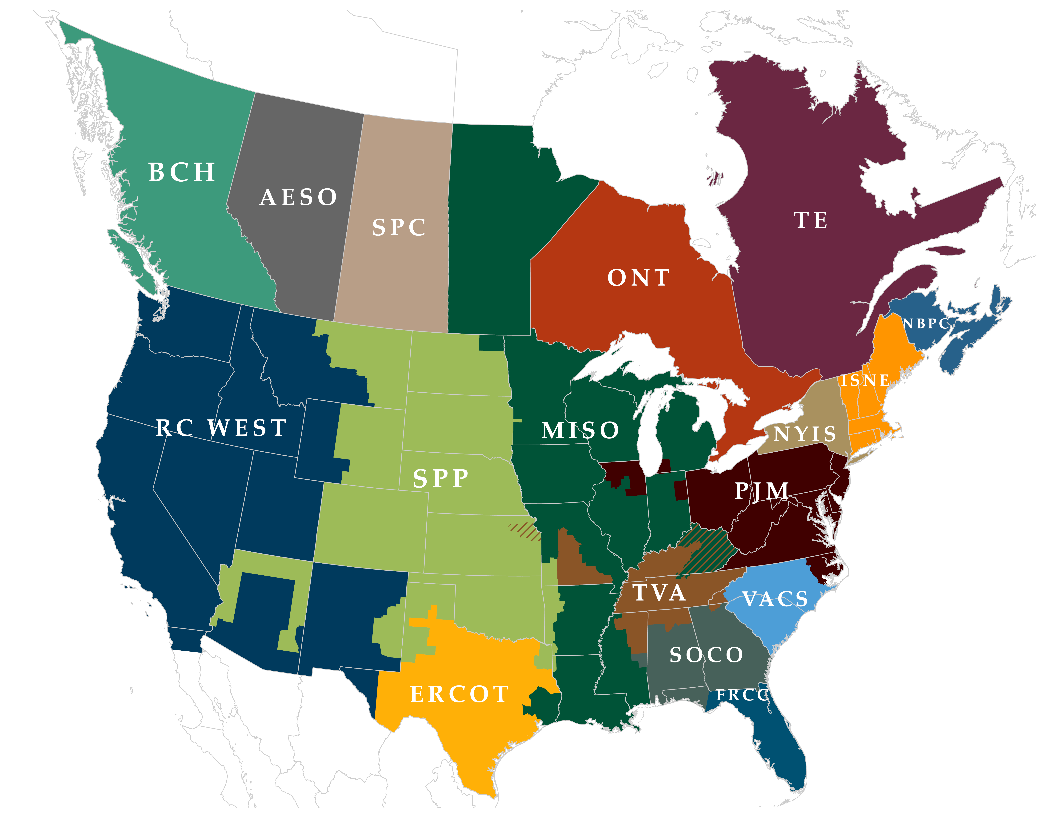
Reliability Coordinators (RC) monitor the grid in real-time and interact with individual operators and other RCs to maintain reliable operations.
Independent System Operators (ISO) and Regional Transmission Operators (RTO) coordinate, control, and monitor parts of the electric grid. ISOs and RTOs may also operate wholesale electricity markets. The Western Energy Imbalance Market (EIM) is a real-time market operated by the California ISO (CAISO). The Western Energy Imbalance Service (EIS) market is a real-time market currently being developed by the Southwest Power Pool (SPP).
.png)
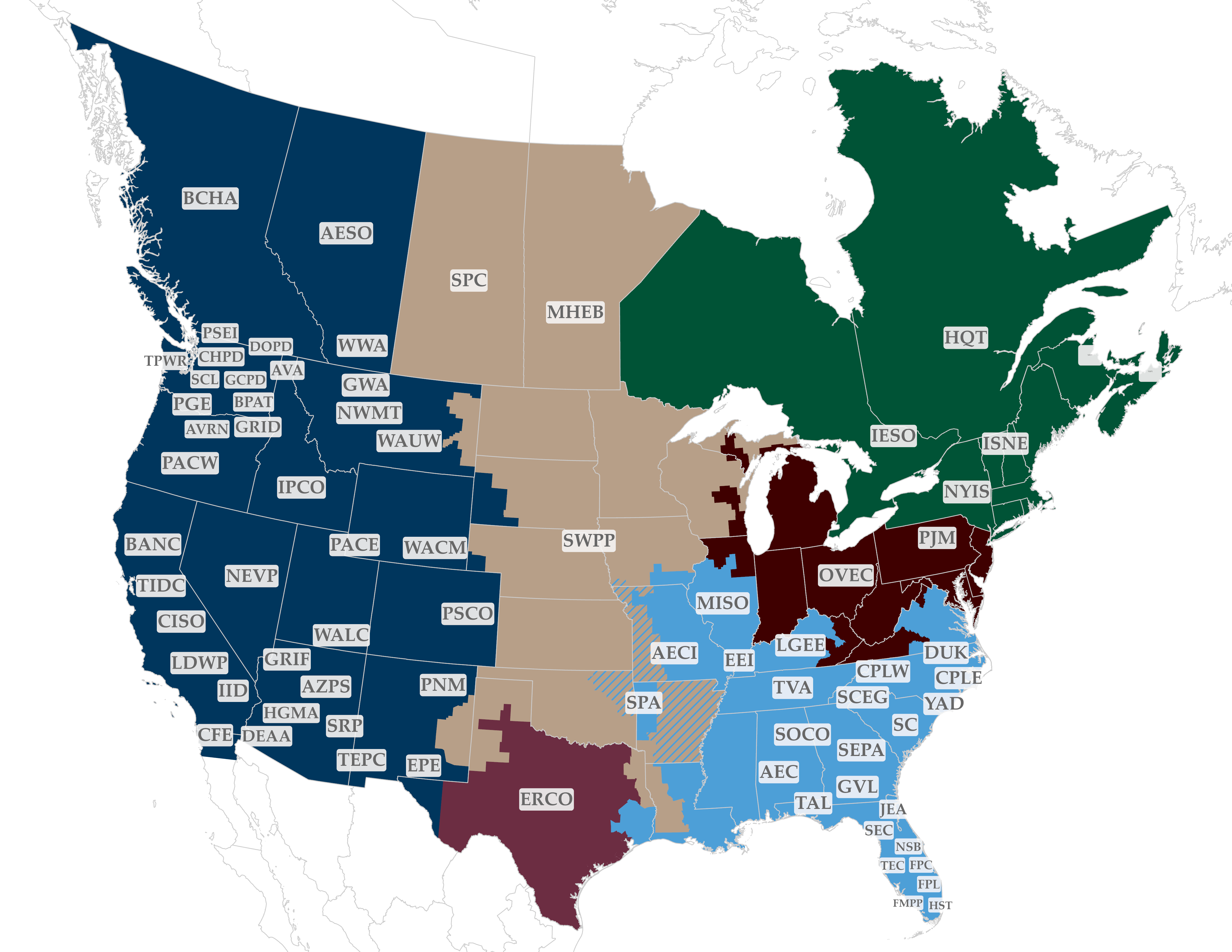
Balancing Authorities (BA) are responsible for maintaining load-generation balance within their footprints.